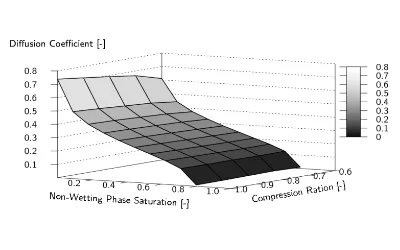
In the current work, we present a comprehensive modeling framework to predict the effective gas diffusivity, as a function of liquid water saturation, based on realistic 3-D microstructures of the uncompressed as well as compressed gas diffusion layer (GDL). The presented approach combines the generation of a virtual microscopic GDL and different physical modeling. We develop a reduced model in order to simulate the compression of the GDL layer since its compression has a strong impact on the material properties such as the water transport or its gas diffusion. Then, we determine the two-phase distribution of a non-wetting fluid, i.e. water, and a wetting fluid, i.e. air, within the GDL for different saturations. This is done using a full morphology (FM) model. Finally, solving the Laplace equation for the partly saturated medium we determine the relative gas diffusion, i.e. the gas diffusion depending on the saturation. In the present work, our approach is applied to a typical GDL medium, a SGL10BA carbon paper.
Numerical Evaluation of Effective Gas Diffusivity - Saturation Dependence of Uncompressed and Compressed Gas Diffusion Media in PEFCs