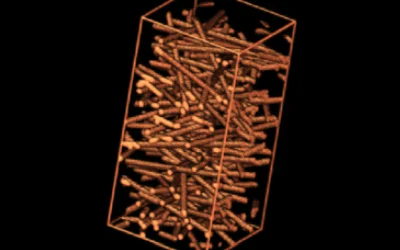
Methods from stochastic geometry allow to construct models which are very good representations of the real complexity of Nonwovens. These realistic models are used as boundaries for a fluid dynamic simulation with a parallel Lattice Boltzmann code, developed by the Fraunhofer ITWM in recent years. As a result, the flow field, the pressure drop across the filter and its permeability are obtained. To study the depth filtration properties, we used a Lagrangian formulation of particle transport in the calculated complex flow field. The relative influence of different filtration mechanisms and the filtration efficiencies of the complex fiber structures are studied as function of particle sizes ranging from D = 2µm. to 4nm. The most penetrating particle size is obtained in good agreement with experiments. For larger particles the clogging of the filter is studied. As an interesting phenomenon, we find often an inhomogeneous loading for particles, even if the particle size is appreciable smaller than typical pore sizes.