Simulation of Air Filtration
The challenge: Effectively separating tiny harmful and diverse particles from the air
Air filtration is a crucial process that protects and enhances the quality of the air we breathe both indoors and outdoors. It removes particles, dust, pollen, bacteria, and viruses, thereby improving overall air quality. Various factors such as pore size, material, and overall design of the filter play a critical role in the efficiency of a filter.
Due to the diverse particle sizes and conditions, optimization is a complex process. Simulations offer significant value in this regard by visualizing the filtration process and providing insights into interactions between particles and filter.
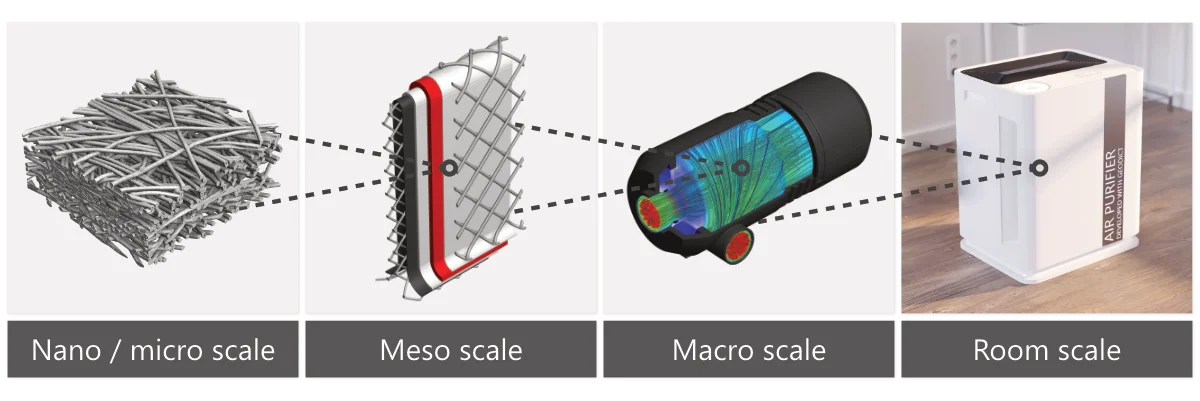
With GeoDict, it becomes possible to visualize, simulate, and optimize the air filtration process at both the micro and macro levels. This includes:
- Permeability determination on the media scale
- Single-pass filtration simulations
- Individual particle size distribution
- Multiscale simulations
- Consideration of electrostatic attraction
- Indoor air simulations
- Systematic parameter studies
As a result, more effective filtration outcomes can be achieved while simultaneously reducing costs in material and energy, leading to a sustainable and significantly faster development cycles for next generation filter.
When simulating flow and filtration on the nano scale using nano fibers the effect of the slip length on the nano fibers needs to be considered. GeoDict is able to set the mean free pass of the given fluid to account for the additional effects at the nano scale. For the usage of micro fibers the effect is neglectable.