Correction of Segmented Images of Granular Microstructures for Accurate Measurement of Mechanical Properties
GeoApp: Contact Correction
A realistic simulation of granular microstructures begins with accurate geometry, typically obtained from micro-CT imaging. For meaningful results, both the field of view (FOV) and the representative elementary volume (REV) are essential. The FOV must cover enough material to capture structural heterogeneity, while the REV defines the smallest volume at which material properties remain consistent.
Meeting these requirements often forces a reduction in image resolution. As a result, thin intergranular gaps disappear in the voxelized data, creating contact zones that appear much stiffer than they are in reality. This distortion alters the local volume field and introduces significant errors in the predicted mechanical properties.
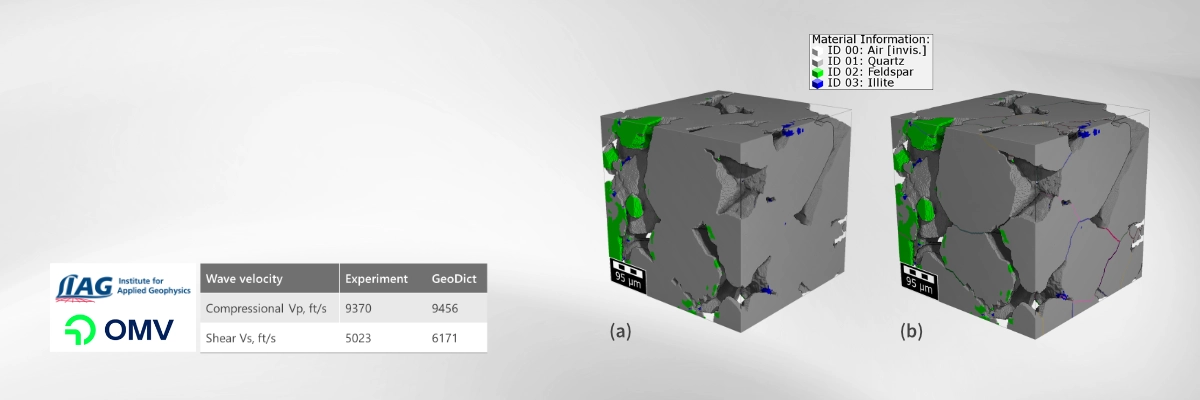
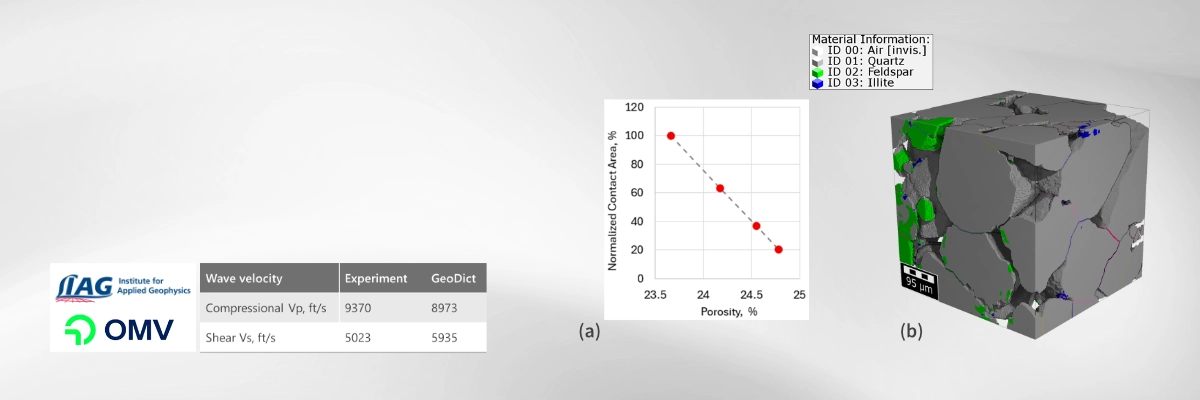
The Contact Correction GeoApp removes these artifacts by correcting segmented contacts, resolving the common overestimation of stiffness caused by limited image resolution, specially in conventional reservoir rocks. Validated against the experimental data in digital rock physics [1], the method also applies to a broad range of grain-based materials, including battery and fuel-cell electrodes, catalyst supports, ceramics, sintered materials, grain packings, and powders.
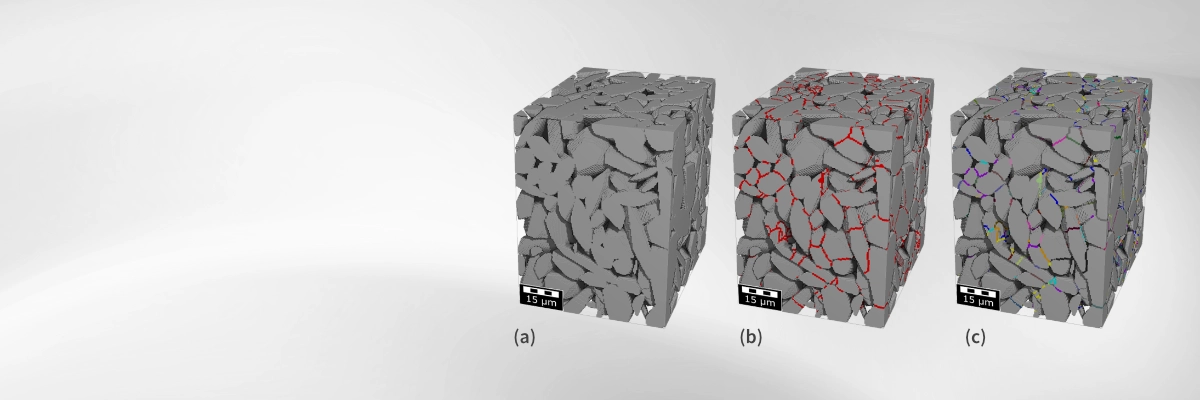
The GeoApp adjusts grain-to-grain contacts to deliver more accurate mechanical property predictions by applying a contact stiffness correction using two robust methods. Both approaches build on the GrainFind watershed-based grain segmentation, which reliably identifies individual grains and their contact zones.
GeoDict Publications
[1] M.Halisch, A.Jacob, O.Lykhachova, G.Burmester, A Novel Grain-Contact Modeling Approach for Enhanced Petro-Elastic Simulations in Digital Rock, SCA-2025. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.16814031
[2] N.Saxena, R.Hofmann, A.Hows, E.H.Saenger, L.Duranti, J.Stefani, A.Wiegmann, A.Kerimov, M.Kabel, Rock compressibility from microcomputed tomography images: Controls on digital rock simulations, Geophasics, Vol.84, No.4, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1190/geo2018-0499.1
Area-dependent method
The Area-dependent Stiffness Reduction method, described in [1], leaves the original segmentation intact but adjusts the mechanical properties to better reflect real behavior. It does so by reducing the effective stiffness according to the relative size of the contact areas between grains.
Explicit method
With the Explicit Contact Area Reduction method [2], contact voxels are physically eroded to reduce the size of contact zones. Because this approach modifies the original structure's porosity, it enables simulations that more closely match experimental conditions, even when the imaging data is limited by resolution.
Modules and GeoApps that are often combined with the Contact Correction GeoApp:
| Import & Image Processing | ImportGeo-Vol |
| Image Analysis | |
| Material Modeling | GrainGeo |
| Simulation & Prediction | ElastoDict |