Model & Simulate in Filtration
FilterDict
Recently, M2M has become active in simulating room air filtration systems and their optimal room placement to increase particle removal efficacy and possibly reduce the risk of viral infection.
Examples of applications for simulations
- Aerosol filtration in a nonwoven filter
- Soot filtration through a honeycomb structure of a Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) or Gasoline Particulate Filter (GPF)
- Oil filtration multi-pass test bench
- Micronic particle filtration and clogging phenomena in microfluidic devices
- Particle tracking through a pleat element
- Clogging of a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter pleat
- Room air purifiers and their placement in the room
Technical Report
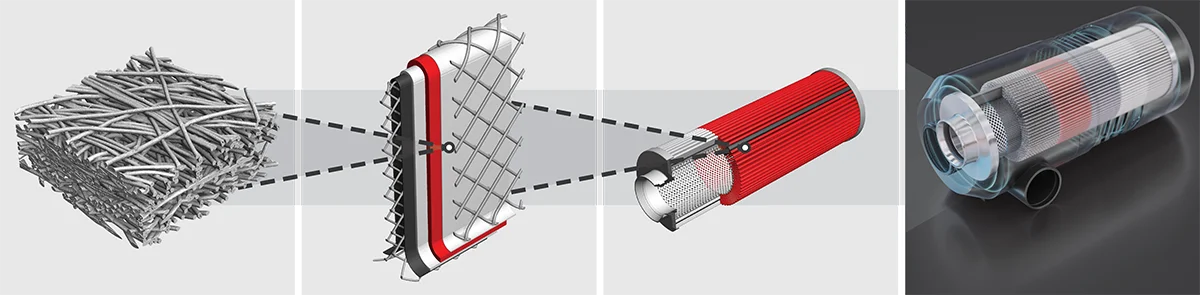
Filtration modeling and simulation with GeoDict, from filter media to filter element
Azimian M., Linden S., Cheng L., Wiegmann A., 2020: Filtration modeling and simulation with GeoDict®, from filter media to filter element, Math2Market GmbH, technical report, https://doi.org/10.30423/report.m2m-2020-03
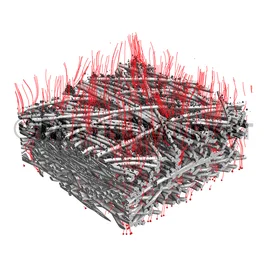
The filter media can be any kind of porous media, typically nonvowen media, woven media (metal, textile, or plastic), foam, membrane (e.g. desalination), or cellulose paper, but FilterDict can also simulate filtration through soil or sand, and others. Any of these filter media can be analyzed, optimized and/or newly designed. Even for nanofibrous filter media, FilterDict simulates filtration accurately by incorporating the slip effect.
With the FilterDict module, filter efficiency computations requiring a single flow field computation can be achieved for realistic nonwoven models (300 x 300 x 600 computational cells) in a few hours. Filter life time simulations may take several days due to the need for re-computing the flow fields.
The prediction of filter efficiency and pressure drop evolution by FilterDict has been extensively validated in a variety of industrial and scientific research projects. The predictions agree with measurements to within 10-20%.
Initial Filter Efficiency - FilterDict determines the filter efficiency and most penetrating particle size (MPPS) of a filter medium by tracking particles through a 3D filter structure. The simulation of the particle movement can include interception, inertial impaction, Brownian motion and electrostatic attraction. Various physical models are available to model the contact of a particle with the filter medium (Caught on first touch, Van der Waals forces / Hamaker constant, Sieving) and allow to model different filtration regimes. User-defined functions allow full control of these model parameters.
Technical Report
Innovative design, analysis and optimization of woven filter media through experimental and computational methods
Azimian M., Mantler A., Meyer F., Edelmeier F., Becker J., Wiegmann A., 2020: Innovative design, analysis and optimization of woven filter media through experimental and computational methods, Math2Market GmbH & HAVER & BOECKER OHG, technical report, https://doi.org/10.30423/report.m2m-2020-02
Technical Report
Improved flow simulations on nanofibrous filter media by incorporating the slip effect
Cheng L., Linden S., Azimian M., Wiegmann A., 2019: Improved flow simulations on nanofibrous filter media by incorporating the slip effect, Math2Market GmbH, technical report, https://doi.org/10.30423/report.m2m-2019-01
The ideal filter has a large Dust Holding Capacity (DHC) and high filter efficiency while maintaining a low pressure drop. These three properties usually depend on each other, meaning that improving one or two of them will usually undermine the third property.
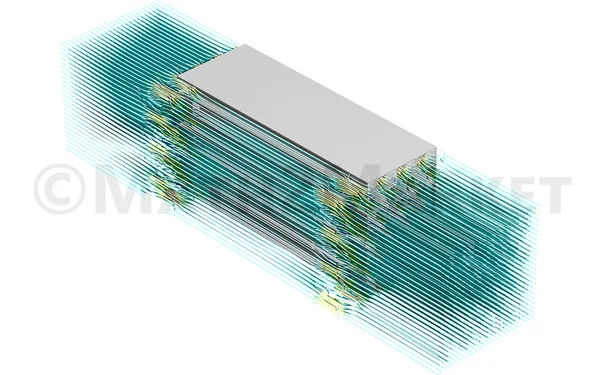
With the goal of increasing the DHC, FilterDict simulates the clogging of a filter in a single pass experiment on the unresolved media (such as single or multiple pleats, pleat elements and diesel particulate filter structures)
Filter elements
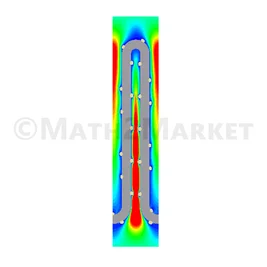
For filter elements such as pleated filters, FilterDict determines filter life-time, pressure drop evolution and fractional efficiencies over time, and DHC.
The filter media of the pleats can be a nonwoven or woven filter media. The pleated filters can be optimized and/or newly designed by choosing flat sheet filter media and specifying the geometry and the number of pleats.
The implemented pass-through model is implemented considers the filtration possibility of each type of particle in different types of unresolved porous media.
The simulation covers the entire filtration regime from depth filtration to cake filtration. The simulation with GeoDict is validated by comparing the results with experiments and adjusting the numerical parameters.
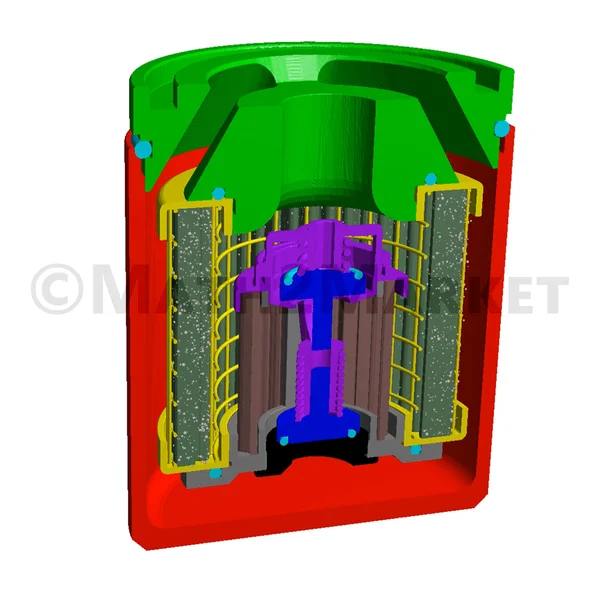
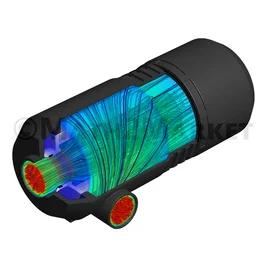
Complete Filters with Housing
For complete filters with housing, the geometry of the parts of the complete filter in CAD format (*.stl and/or .obj) is imported and converted into a GeoDict voxel (3d pixel) using the ImportGeo-CAD module. The user defines inlet and outlet for the flow and the characteristics of the filter parts (flowing fluid, solids, porous parts). The characteristics of the filter media at micro scale are also defined (e.g., permeability).
The filter media of the pleats inside the complete filter can be a nonwoven or woven filter media.
The lifetime single-pass simulation determines the changes in pressure drop as a function of time, the fractional filtration efficiencies, and the deposited dust per batch.
Honeycomb Structures
For honeycomb structures, such as in Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF) und Gasoline Particulate Filters (GPF), FilterDict is used to design and optimize the filters for lower pressure drop, higher filter efficiency and longer life time.
The simulation steps ( Azimian et al., 2018) include
- modeling the ceramic filter media (GrainGeo),
- simulating the air flow through the filter media (FlowDict) and the transport and deposition of soot particles (FilterDict),
- the conversion of deposited particles into a porous media, and
- determining the soot layer's packing density and viscous flow resistivity.
The simulation of gas filtration at the molecular level can be simulated with the AddiDict module.
| Modules | Applications |
|---|---|
| GeoDict Base | includes the basic functionality of GeoDict [necessary] |
| FlowDict | computes flow fields as well as the pressure drops or mean velocities [necessary] |
| ImportGeo-Vol | import and segmentation of the µCT images and generation of the 3D microstructure models based on them [optional] |
| Digital Material Design | for filter media: creating and modeling 3D microstructure models in GeoDict [optional] |
| PleatGeo | for pleat elements: generation of unresolved porous media [optional] |
| GridGeo | for honeycomb structure models: generation of unresolved porous media [optional] |
| ImportGeo-CAD | for complete filter with housinge: Import of STL or OBJ files of the housing and convert them to voxel data for the simulation [optional] |