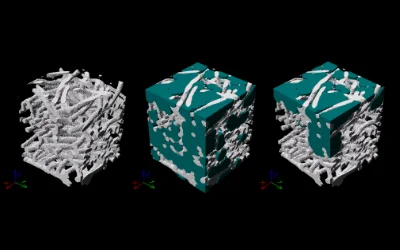
In most flow simulations of fuel cells the gas diffusion layer is modeled as homogenised porous medium. The properties of this porous medium are described by saturation and compression dependent parameters: capillary pressure, permeability, diffusivity and heat conductivity. In this talk we will present a numerically efficient approach to determine these material parameters. Starting from a 3D tomography image of a gas diffusion layer or a 3D stochastical model of the fibre structure the distribution of gas and water phase is determined using the pore morphology method [1]. Using these 3D phase distributions, we are able to determine permeability, diffusivity and heat conductivity as a function of the saturation of the porous media with comparatively low numerical costs. Using a simple model for the compression of the gas diffusion layer, the influence of the compression on the parameter values is studied.