Transform and Optimize 3D Voxel Images
ProcessGeo
The ProcessGeo module is a core component of GeoDict’s image modification toolkit, working in tandem with LayerGeo to enable precise editing and transformation of 3D voxel-based geometries. With ProcessGeo, users can perform a wide range of manipulations to optimize material models created from imported µCT or FIB/SEM scans (via ImportGeo-Vol) or generated using other GeoDict digital material design modules like GrainGeo, FoamGeo or FiberGeo.
ProcessGeo enables users to reshape geometries, precisely adjust them, and purposefully optimize them so that models exactly meet the desired specifications and are perfectly prepared for subsequent analyses. ProcessGeo is frequently combined seamlessly with LayerGeo to create complex, multiphase structures before detailed material properties are then evaluated using the corresponding digital analysis modules such as FlowDict or PoroDict.
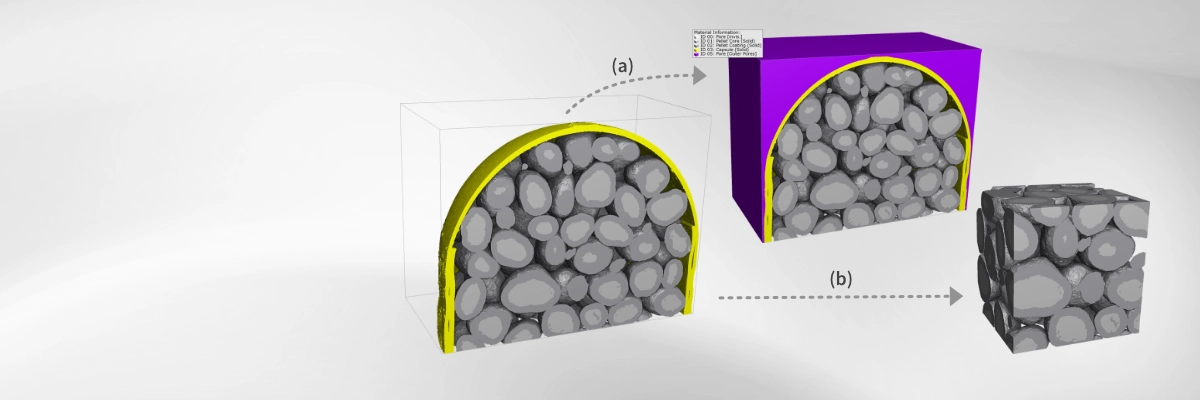
Crop reduces the 3D image to a defined region of interest (ROI), removing irrelevant areas such as empty space outside the material—essential for efficient and accurate flow simulations. Embed, in contrast, expands the image by adding features like inlets or outlets, for example to prepare a geometry for filter simulations.
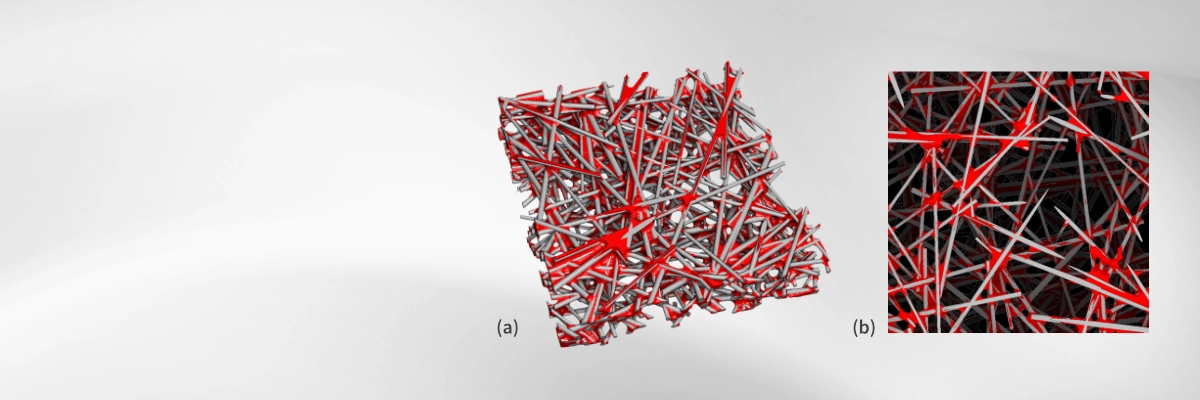
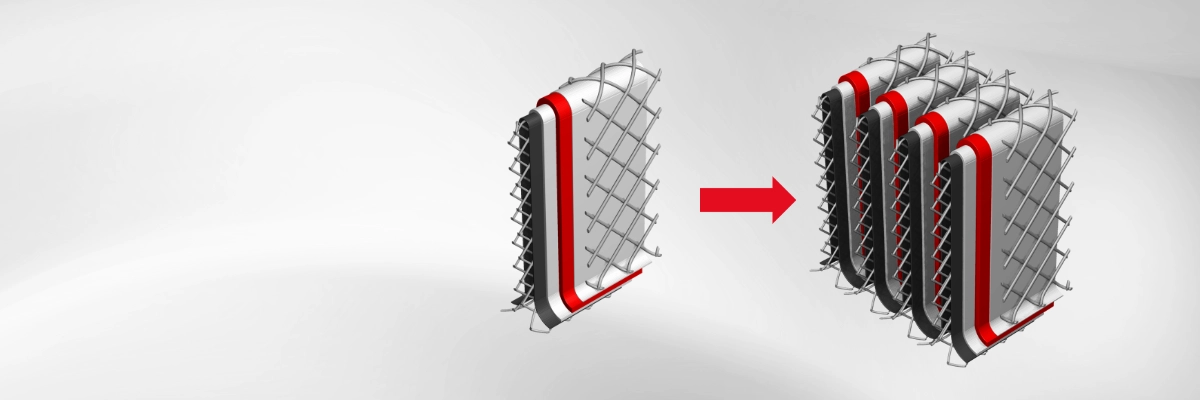
Mirror and Repeat can extend a geometry by reflecting or replicating it along selected axes. These operations are useful for creating symmetric structures, larger simulation domains or to model periodic boundary conditions.
Assigning the correct constituent materials—and therefore the correct material properties—is critical for achieving accurate simulation results. This can be done using Reassign Material ID, which changes the voxel label of a region, and Reassign Material, which directly updates the associated material properties. These tools ensure that the geometry reflects its true physical characteristics, enabling realistic performance predictions in subsequent analyses.
Dilate and Erode modify the geometry by expanding or contracting material phases at the voxel level. Dilate increases the extent of a phase, useful for closing small gaps or strengthening connections, while erode reduces a phase, helping to remove thin bridges or isolate features. These operations are often applied to refine scan data, adjust pore sizes, or prepare geometries for more stable and representative simulations.
Cleanse Structure removes small, unwanted components that may result from the import process and represent artefacts rather than true material features. Eliminating these artefacts is essential for ensuring clean, accurate geometries, as their presence can interfere with subsequent simulations—such as reducing the precision of flow computations performed with FlowDict.
With Add Binder, it is possible to add realistic binder distributions to an existing 3D microstructure model. The binder distribution may be anisotropic, and it can follow a gradient distribution.
Flood Fill Large Pores identifies and separates large pore regions from smaller pores within a 3D structure. This is particularly useful for distinguishing interior pores from exterior void spaces, for example in the analysis of a tablet model. By clearly differentiating these regions, the operation enables more accurate structural characterization and targeted analysis of pore size distribution.
Invert Structure swaps material and pore space within the geometry, enabling alternative analyses such as studying void networks instead of solid phases. Create Empty Structure generates a fully void domain of specified dimensions, serving as a blank canvas for building new geometries or embedding existing ones.
Permute, Rotate and Mirror operations reorient a 3D voxel image to match analysis requirements, such as aligning the structure with the flow direction in FilterDict or the charging axis in BatteryDict. Correct orientation ensures simulations reflect physically relevant conditions and yield more accurate, comparable results.
Compress reduces the void or pore space in the 3D image, thereby increasing the solid volume percentage (SVP). This operation can be used to model the slight compression of structures such as nonwoven materials or gas diffusion layer (GDL) geometries. Mark Components detects and labels discrete, connected regions within the structure, making it possible to perform targeted modifications, conduct phase-specific analyses, or isolate individual areas for further study.
Rescale adjusts the resolution of a 3D image by increasing or decreasing the voxel size. This allows either finer details for more accurate simulations or a coarser resolution to reduce computational demands.